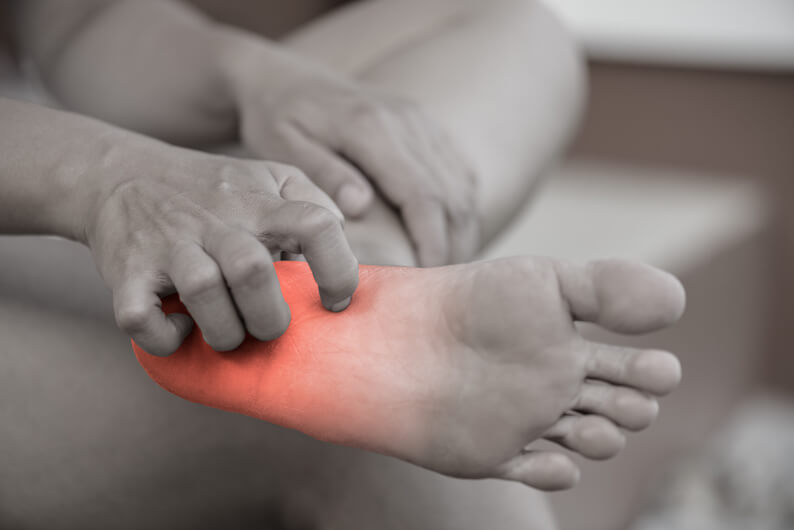
Understanding Neuropathy
Neuropathy, often referred to as peripheral neuropathy, is a term used to describe a group of disorders that result from damage to the peripheral nerves. These nerves are responsible for transmitting signals between the central nervous system (the brain and spinal cord) and the rest of the body, including the limbs, skin, and internal organs. When these nerves are damaged, they send abnormal signals to the brain, leading to a wide range of symptoms.
The leading cause of neuropathy is diabetes. Poorly managed diabetes (blood sugar) accounts for roughly 60 percent of the total number of people with neuropathy.
“Most of the patients develop symptoms after 10 years of being diagnosed with diabetes mellitus,” said VIPcare primary care provider Dr. Richard Santiago. “All depends on how well the diabetes is controlled.”
Common Warning Signs of Neuropathy
Neuropathy can be displayed in a variety of ways and symptoms. This often leads to neuropathy being mistaken for some other condition, such as fibromyalgia. However, there are specific warning signs of neuropathy you should take notice of if present.
“Almost all the symptoms are on lower extremities,” said Dr. Santiago. “The symptoms that I’m looking at are pain, burning sensation, tingling, numbness, and unbalance.”
- Numbness and Tingling: One of the earliest and most common signs of neuropathy is a sensation of numbness or tingling, often described as a “pins and needles” feeling. This can occur in the hands, feet, arms, or legs.
- Burning Sensation: Individuals with neuropathy may experience a persistent burning or electric shock-like sensation in the affected areas.
- Loss of Sensation: As neuropathy progresses, some individuals may notice a decreased ability to feel temperature changes, pain, or touch in the affected areas.
- Muscle Weakness: Neuropathy can lead to muscle weakness or a feeling of heaviness in the limbs, making it difficult to perform everyday tasks.
- Balance Issues: Nerve damage can affect proprioception (the sense of body position), leading to balance problems and an increased risk of falls.
- Pain: Neuropathic pain can range from mild discomfort to severe shooting pain. It may be constant or intermittent and can significantly impact a person’s daily life.
- Difficulty Walking: As neuropathy progresses, some individuals may experience difficulty walking or have an unsteady gait.
- Changes in Reflexes: Neuropathy can affect reflexes, leading to abnormally brisk or diminished responses.
- Sensitivity to Touch: Some individuals may become hypersensitive to touch, experiencing pain or discomfort even from gentle contact.
- Digestive Issues: Neuropathy can affect the nerves controlling the digestive system, leading to symptoms such as bloating, constipation, diarrhea, or difficulty swallowing.
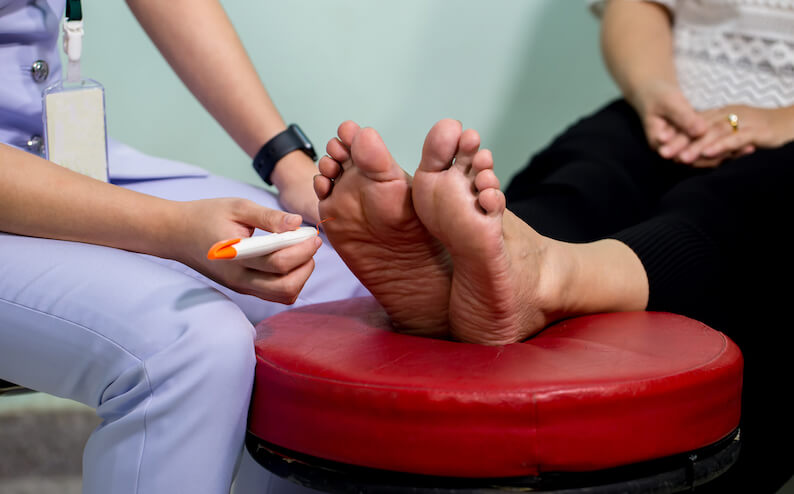
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you experience any of the above warning signs of neuropathy, it’s essential to seek medical attention immediately. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent further nerve damage and improve overall outcomes.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing neuropathy involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests such as nerve conduction studies and electromyography. Identifying the underlying cause of neuropathy is crucial for effective treatment.
Treatment options may include:
- Medications: Depending on the cause and severity of neuropathy, providers may preseribe pain relievers, anticonvulsants, and antidepressants to manage symptoms.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy exercises can help improve muscle strength, balance, and coordination.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Lifestyle changes, including managing blood sugar levels (for diabetic neuropathy), maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding alcohol, can help slow the progression of neuropathy.
- Pain Management Techniques: Techniques such as acupuncture, massage, and transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) may provide relief from neuropathic pain.
- Underlying Condition Treatment: Addressing the underlying cause of neuropathy, such as diabetes or vitamin deficiencies, is essential to prevent further nerve damage.
“It’s very important to start in the early stages of the diagnosis,” said Dr. Santiago about neuropathy management. “Keep A1c levels at seven or less. Fasting blood sugar at least at 130 mg/dl. Do exercise. Healthy diet. Keep a good weight and take B complex with folic acid. Also, it’s very important to keep regular follow up with your PCP.”
Neuropathy is a complex and often debilitating condition that can have a significant impact on your well-being. By recognizing the warning signs of neuropathy and seeking medical attention as soon as you develop symptoms, you can take proactive steps to manage the condition and improve your quality of life. Prevention and early intervention are key to better outcomes and Better Health. Contact your primary care provider for proper evaluation, diagnosis, and guidance on managing your neuropathy.
 About Dr. Richard Santiago
About Dr. Richard Santiago
Dr. Richard Santiago is a primary care physician specializing in family medicine. He graduated with a degree in biology from the University of Puerto Rico before attending Autonoma University of Guadalajara in Mexico to earn his medical degree. Learn more